Print finishing is an art in itself and it helps bring designs to life on paper and give them an extra push to go from good to great. There are so many possibilities and options to choose from. Prices vary based on these various print techniques and finishes.
Below are information on the available print finishes that we can provide you;
 Lamination adds a layer of protective coating (usually some type of plastic), often glossy or matte, to the printed surface while also improving its sturdiness and water resistance.
Lamination adds a layer of protective coating (usually some type of plastic), often glossy or matte, to the printed surface while also improving its sturdiness and water resistance.
With high gloss laminated printed surfaces, photos and images appear to have more contrast and have better sharpness, while with Matte lamination, prints are more subdued but it adds a luxurious and elegant finish to the printed surfaces.
Paper varnishes on the other hand are applied to paper stock to give the page a smooth and consistent texture as well as having the added benefit of sealing the printed material to help preserve it better. It can also either be matte or gloss. Typically, varnishes are applied to the entire printing surface when a page needs to be robust but without adding too much weight to the paper stock, making it suitable for magazine pages, magazine covers, and brochures.
Lamination and varnishes are not very different; either can be used depending on the desired outcome.
 Spot UV varnishes are paper varnishes applied to the printing surface and is cured or hardened by UV light during the printing process. This results in a glossy coating on the surface of your print, it is usually referred to as Spot Lamination.
Spot UV varnishes are paper varnishes applied to the printing surface and is cured or hardened by UV light during the printing process. This results in a glossy coating on the surface of your print, it is usually referred to as Spot Lamination.
UV varnishes are usually used as a spot application where only specific parts of the page get a UV varnish. It is used to effectively give texture and focal interest to different areas of the printing surface while leaving other areas untreated.
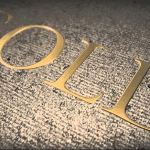 Foil stamping is the use of a malleable metallic material applied to the print surface by using heat and pressure.
Foil stamping is the use of a malleable metallic material applied to the print surface by using heat and pressure.
It is used to add reflective properties to various elements of your design and can serve to add a bit of luxury to your project.
It looks really great on texts and logos or other certain elements and it is available in a wide variety of colours.
 Generally, embossing refers to raising parts of the page for emphasis and texture.
Generally, embossing refers to raising parts of the page for emphasis and texture.
This print finish adds physical depth to the embossed elements and thus, shadows and highlights are also produced in the design.
Embossing also adds a tactile dimension to your design. Images and text are literally felt.
It is often combined with other print techniques such as foil stamping to enhance the effects of both techniques. It is usually referred to as Blind embossing.
 Letterpress printing is one of the oldest printing techniques available. Some printers may call letterpress printing by the term debossing or engraving.
Letterpress printing is one of the oldest printing techniques available. Some printers may call letterpress printing by the term debossing or engraving.
A letterpress is used to depress or indent certain portions of the page. It can be seen as the opposite of embossing.
 White is the absense of colour , so until now to print white you reverse print by not printing anything within the letterforms , just around them as a background. Then came the new innovation of white ink printing where white ink is actualy printed on transparent materials and coloured stocks.
White is the absense of colour , so until now to print white you reverse print by not printing anything within the letterforms , just around them as a background. Then came the new innovation of white ink printing where white ink is actualy printed on transparent materials and coloured stocks.
It does not only improve the look and quality of your prints but also gives it a sort of avant garde effect
 Without the need for the plates and make-ready of traditional flat printing, digital printing allows for “on demand”, short turn around and cost effective low quantity runs.
Without the need for the plates and make-ready of traditional flat printing, digital printing allows for “on demand”, short turn around and cost effective low quantity runs.
 Thermography is a process which applies a plasticized to offset ink while it’s still wet on the paper. Under high heat the powder melts only over the wet ink, resulting in a raised effect. It is usually called Powder embossing
Thermography is a process which applies a plasticized to offset ink while it’s still wet on the paper. Under high heat the powder melts only over the wet ink, resulting in a raised effect. It is usually called Powder embossing
 A process by which a metal die cuts paper under pressure to replicate art or various shapes, usually along the material’s edges. They are not as intricate as laser cutting designs.
A process by which a metal die cuts paper under pressure to replicate art or various shapes, usually along the material’s edges. They are not as intricate as laser cutting designs.
 Laser cutting is a type of subtractive manufacturing that cuts a digital design file into a piece of sheet material. They range from simple to extremely intricate cuts.
Laser cutting is a type of subtractive manufacturing that cuts a digital design file into a piece of sheet material. They range from simple to extremely intricate cuts.